accuracy
The closeness of agreement between a result and the accepted reference value. Accuracy, when applied to a set of test results, involves a combination of random components and a common systematic error or bias component.
active rule
A SPC rule or analytical goal with a status of warn or reject.
Affiliated Data Exception Report
Note: Affiliated Reports are optional. Contact your Bio‑Rad QC Program Representative to request Affiliated Reports.
For all laboratories within the affiliated laboratory consensus group, this report shows any analyte:
affiliated group
A group of laboratories in the Unity™ Interlaboratory Program comparing their results and essentially become their own consensus group. Contact your Bio-Rad QC Program Representative to request any of the available Affiliated Reports.
Affiliated Laboratory Comparison Report
Note: Affiliated Reports are optional. Contact your Bio‑Rad QC Program Representative to request Affiliated Reports.
The Affiliated Laboratory Comparison Report summarizes the performance of each participating affiliated laboratory in a single report. Statistics are provided for your laboratory and all affiliated laboratories and include:
Affiliated Laboratory Comparison Report: Abbreviated Summary
Note: Affiliated Reports are optional. Contact your Bio‑Rad QC Program Representative to request Affiliated Reports.
This report is designed for a quick review and focuses on key statistics to provide a performance summary for multiple laboratories. This report summarizes the performance of each participating affiliated laboratory in a single report. For each test, this report shows:
Affiliated Reports
Note: Affiliated Reports are optional. Contact your Bio‑Rad QC Program Representative to request Affiliated Reports.
Affiliated Reports allow a group of laboratories to compare results, essentially creating their own consensus group. The Unity™ Interlaboratory Program provides the following Affiliated Reports:
all labs group
One of the available Unity™ Interlaboratory Program consensus groups. The All Labs consensus group is composed of data from all laboratories reporting for the same lot number, level, units, and temperature of a test.
analyte
A substance or chemical constituent being analyzed such as glucose, TSH, and so on.
analytical goals
Analytical goals are used as a retrospective review tool in conjunction with SPC rules and can optimize the QC effort and cost. Analytical goals are configured on a test-by-test basis; only one analytical goal can be used at a time. The following analytical goals are available in Unity Real Time™ online:
analytical process
A series of steps taken in the analysis or testing of patient specimens or samples.
audit trail
A secure, computer generated electronic record allowing reconstruction of the course of events relating to the creation, modification, and deletion of an electronic record.
bias
Bias measures how far an observed value is from a target value and is expressed as a percentage. Bias is determined by a reference value or estimated from an outside source such as proficiency testing results or the Bio-Rad Unity™ Interlaboratory Program. Use the following formula to calculate bias:

Note: Bias is the total systematic error as contrasted to random error. There may be one or more systematic error components contributing to the bias. A larger systematic difference from the accepted reference value is reflected by a larger bias value. [ISO 3534-I]
Bias and Imprecision Histogram Report
The Bias and Imprecision Histogram Report is one of the Unity™ Interlaboratory Reports. This report provides a graphic representation of a laboratory's bias compared to the current cumulative consensus group mean and a laboratory's CV. On the chart, the monthly CV is represented as a bar and the bias is represented as a diamond with lines connecting each diamond. The Bias and Imprecision Histogram Report helps to detect changes in performance over time and to identify if the change in performance is due to imprecision, bias, or both.
Note: The Bias and Imprecision Histogram Report does not contain specific thresholds for allowable bias or allowable imprecision.
CLIA
Acronym for the Clinical Laboratory Improvements Amendments of 1998 which regulate laboratory practice in the United States.
CLSI
Acronym for the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Formerly the NCCLS.
consensus group
A group of laboratories submitting data to the Unity™ Interlaboratory Program. Carefully select a consensus group for comparison as statistical outcomes can be quite different based on the nature of the grouping. When choosing a consensus group, always choose the most specific group for which statistics are available.
The available Unity™ Interlaboratory Program consensus groups are:
The Peer consensus group is composed of all laboratories using the same instrument, lot number, level, reagent, analytical method, units, and temperature of a test. This is the ideal group for comparison.
The Method consensus group is composed of all laboratories using the same lot number, level, analytical method, units, and temperature of a test. Use the Method group if there is an insufficient number of laboratories in the Peer group.
The All Labs consensus group is composed of data from all laboratories reporting for the same lot number, level, units, and temperature of a test.
cumulative mean
Also known as floating mean. The mean of all accepted data points entered for a test. If a fixed mean is not defined, the software uses the cumulative (floating) mean for rule evaluation.
CV (coefficient of variation)
The coefficient of variation is the standard deviation expressed as a percentage of the mean. Use the following formula to calculate the CV:
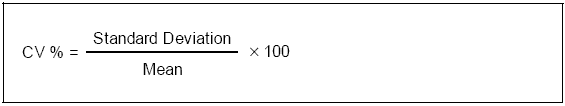
CVR (coefficient of variation ratio)
The coefficient of variation ratio compares a laboratory's precision to that of other laboratories in a consensus group. Use the following formula to calculate the CVR:

data group
A user-defined set of data points having something in common, such as a calibrator lot. Define data groups on the Single Test Point Data Entry dialog box and the Single Test Summary Data Entry dialog box.
Data Rejection Report
The Data Rejection Report is one of the Unity™ Interlaboratory Reports and is only generated when data is rejected by the Unity™ Interlaboratory Program. The rejected data points are not included in cumulative statistics or in statistical comparisons. Data points may be rejected for two reasons:
data set
A group of data points having some elements in common (for example, the lab or lot numbers, panel assignments, data entry dates, and so on). Use data sets to compare data on the Data Analysis Grid and to determine the scaling (mean and ±3SD range) of the Y-axis on the Levey-Jennings Chart, Bar Chart, Youden Chart, and Yundt Chart.
evaluation mean/SD
The mean and SD Unity Real Time™ online uses to evaluate a data point. When using cumulative (floating) statistics, these values can be different for each data point. View the evaluation statistics by clicking ![]() for a row of data on the Single Test Point Entry dialog box.
for a row of data on the Single Test Point Entry dialog box.
fixed statistics
Fixed statistics refers to specifying (fixing) the evaluation mean and/or SD for a test.
floating mean
Also known as cumulative mean. The mean of all accepted data points entered for a test. If a fixed mean is not defined, the software uses the floating (cumulative) mean for rule evaluation.
imprecision
Imprecision is a term to describe the dispersion or spread of a set of values about the mean value of a normal or gaussian distribution. It is usually expressed as a SD or CV.
Imprecision-BV
An analytical goal targeting test imprecision based on biological variation data and laboratory-selected performance goals. Imprecision-BV is based on published "within-subject" biological variation data, rather than consensus group performance. Imprecision-BV can be used for any analyte for which limits are published.
inactive rule
A SPC rule or analytical goal rule with a status of off.
InstantQC™
An instant laboratory program option for comparing point data submitted via the Bench Review or Supervisor Review to other laboratories' data on demand. InstantQC™ Reports and Charts are available on www.QCNet.com.
InstantQC™ Chart
When sending data to the Unity™ Interlaboratory Program from Bench Review or Supervisor Review, the reviewed data points appear on InstantQC™ Reports and Charts on www.QCNet.com after a short processing time. The InstantQC™ Chart plots your data points for your selected date range against your selected consensus group's mean and ±3SD range.
InstantQC™ Report
When sending data to the Unity™ Interlaboratory Program from Bench Review or Supervisor Review, the reviewed data points appear on InstantQC™ Reports and Charts on www.QCNet.com after a short processing time. The Comparison Statistics Shown are:
interlaboratory
Comparative results between laboratories used to determine values and assess test methods.
intralaboratory
Within a single laboratory.
Laboratory Comparison Report
The Laboratory Comparison Report is one of the Unity™ Interlaboratory Reports and shows the monthly and cumulative statistics for the laboratory, Peer group, and Method group for all tests reported. The Laboratory Performance Overview Report is automatically generated each month you submit data; however, you can specify a different report frequency. See Configure Unity™ Interlaboratory Report Frequency for more information.
Use the Laboratory Comparison Report to compare results to those of the Peer and Method consensus groups. For VITROS® instruments, the Laboratory Comparison Report provides statistics for the laboratory, Peer group, and Method group based on the slide generation numbers reported for the laboratory.
The Laboratory Comparison Report contains the following monthly and cumulative statistics for each test:
The Laboratory Comparison Report also contains the monthly and cumulative Peer and Method group statistics for:
Laboratory Histogram Report
The Laboratory Histogram Report is one of the Unity™ Interlaboratory Reports and is a bar chart showing up to a 12 month summary of the laboratory's monthly means against the current cumulative consensus group means ±2SD range. The Laboratory Histogram Report is automatically generated each month you submit data; however, you can specify a different report frequency. See Configure Unity™ Interlaboratory Report Frequency for more information.
The report shows the laboratory's mean, SD, CV, and number of points for each bar. Each level of control has a separate bar chart.
The Laboratory Histogram Report provides a visual comparison which is useful to identify shifts (abrupt changes in values) and trends (gradual changes in values).
Laboratory Performance Overview Report
The Laboratory Performance Overview Report is one of the Unity™ Interlaboratory Reports and allows you to visually evaluate the bias and imprecision for each test compared to the Peer and Method consensus groups on a modified Youden Chart. The Laboratory Performance Overview Report is automatically generated each month you submit data; however, you can specify a different report frequency. See Configure Unity™ Interlaboratory Report Frequency for more information.
The SDI and CVR are combined as X-Y coordinates located within one of three performance zones designated by increased levels of shading:
Acceptable performance.
Acceptable to marginal performance. This may indicate the need to investigate test system bias and imprecision.
Outside of acceptable and marginal performance.
Corrective action may be needed.
Unacceptable performance.
Requires corrective action.
The center of the graph (SDI and CVR both equal to zero) represents perfect agreement between the laboratory's values and the consensus group (Peer or Method) statistics. Bias and imprecision increase as values move further away from the center of the graph.
level
When referring to QC materials, level refers to the concentration of analytes within the control material. Controls are usually bi-level (low and high) or tri-level (low, normal, and high).
levels in use
The levels of a control product used in the laboratory (for example, level 1, level 2, level 3). Unused levels of a control material are omitted from intralaboratory and Unity™ Interlaboratory Reports.
Levey-Jennings Chart
A graphical chart used to plot successive quality control results, either day-to-day or run-to-run.
Manufacturer Report
The Manufacturer Report is provided through the Unity™ Interlaboratory Program and is a subset of the information from the Worldwide Report separated by the instrument manufacturer. The Manufacturer Report is a good reference to use when evaluating a new instrument or kit and is updated every month.
master lot number
For Bio-Rad controls, the master lot number is the 5-digit lot number, ending in zero, which includes all levels of the control product (for example, 40910). To identify the levels of a control product, the final zero is changed to the level number (for example, 40911 is level 1, 40912 is level 2, and 40913 is level 3).
matrix
The substance containing the analyte being tested (for example, serum, urine, spinal fluid, whole blood).
maximum QC
The condition existing when Westgard Advisor™ online is unable to suggest rules meeting your quality specification (TEa). This condition indicates the test process has such a low process capacity (high total error) it cannot be controlled to a defined level of quality. The default maximum QC procedure is a Westgard multirule applying every possible rule.
mean
The mean for a group of data points is simply the arithmetic average. The mean provides a laboratory's best estimate of the analyte's "true" value for a specific level of control. The mean ± a predetermined number of standard deviations represents the error expected in a test when the analytical system is stable. Use the following formula to calculate the mean:

median
The middle value in a distribution, above and below which lie an equal number of values.
Medical Relevance
An analytical goal described as the total error that would cause a clinician to change a patient's diagnosis, prognosis, or treatment plan. This is based on confirming test imprecision within specified limits. Medical Relevance can distinguish statistical error from medically important changes when used as a feedback tool.
method
The way by which an analyte is measured (for example, hexokinase).
method group
One of the available Unity™ Interlaboratory Program consensus groups. The Method consensus group is composed of all laboratories using the same lot number, level, analytical method, units and temperature of a test. Use the Method group when there is an insufficient number of laboratories in the Peer group.
Monthly Evaluation Report
The Monthly Evaluation Report is automatically generated each month you submit data. The Monthly Evaluation Report validates the monthly laboratory performance as compared to the Peer group. This report identifies when the monthly laboratory performance does not statistically compare with or was not accepted into the Unity™ database. Also, the Monthly Evaluation Report notifies the laboratory when its data was not received in time for the comparison.
operating point
The point on an OPSpecs Chart representing the intersection of bias and imprecision for a test. The Operating Point represents the current performance of a test.
OPSpecs (operational process specifications) Chart
OPSpecs Charts are an integral part of Westgard Advisor™ online. In general, an OPSpecs Chart is a tool for assisting a laboratory to select appropriate SPC rules and the number of control measurements for a QC procedure. OPSpecs Charts are plots of the allowable inaccuracy versus allowable imprecision. The highest line on the chart describes the maximum limits for inaccuracy and imprecision for a stable process. The lower line describes operational limits with the selected QC procedure. The Operating Point appears where the accuracy and precision of the test intersect.
panel
A user-defined group of tests organized to make data entry and review easier. Create a panel to customize the organization of tests in a convenient way. For example, a panel can be created to group a number of different tests performed on a single instrument, or a panel can be created to group the same test performed on multiple instruments.
peer group
One of the available Unity™ Interlaboratory Program consensus groups. The Peer consensus group is composed of all laboratories using the same instrument, lot number, level, reagent, analytical method, units, and temperature of a test. This is the ideal group for comparison.
percent AQA (SE)
The percent of analytical quality assurance (AQA) for systematic error (SE) is the chance of detecting medically important systematic errors. Percent AQA (SE) is synonymous with probability of error detection (Ped).
point data
A single value generated as a result of testing an analyte within a control material.
precision
A measurement of how close a set of measurements are to each other. The measurements may or may not be close to the "true" answer. See "accuracy".
probability of false rejection (Pfr)
A QC performance characteristic describing how often a run is rejected when there are no errors.
pupil
The inner circle on a Yundt plot representing the smaller CVR of two data sets.
QC (quality control)
In the clinical laboratory, QC is a system designed to increase the probability each result report is valid and can be used with confidence by a health care provider when making diagnostic or therapeutic decisions.
random error
A random deviation from the laboratory mean. "Expected" or "acceptable" random error is generally between ±3SD of the mean. A deviation greater than ±3SD is considered "unacceptable" random error. Because of its random nature, this type of error is unpredictable.
range
The difference between the largest and the smallest observed value of a quantitative characteristic or statistical limit.
rejection rule
A SPC rule with a status of reject. When a data point violates a SPC rule with a reject status, the point is not accepted and is excluded from monthly and cumulative statistics and is not reported to the Unity™ Interlaboratory Program for consensus group comparison.
run
A set of QC values Unity Real Time™ online groups together for statistical profile rule evaluation (for example, within run and between run).
shift
A type of systematic error evidenced by an abrupt change in the mean of the control values.
SD (standard deviation)
The standard deviation measures a test's precision, or how close individual measurements are to each other. (The standard deviation does not measure bias, which requires comparing results to a target value such as the Peer consensus group.) The standard deviation provides an estimate of how repeatable a test is at specific concentrations. Test repeatability can be consistent (low standard deviation, low imprecision) or inconsistent (high standard deviation, high imprecision). Use the following formula to calculate the SD:

SDI (standard deviation index)
The standard deviation index is a measurement of bias (how close a value is to the target value). The Unity™ Interlaboratory Program uses the consensus group value as the target value. Use the following formula to calculate the SDI:

SPC (statistical process control) rules
A set of rules which use statistics to monitor and evaluate a process. SPC rules include the original six Westgard rules as well as additional rules.
Statistical Profile Report
Note: The Statistical Profile Report is optional. Contact your Bio‑Rad QC Program Representative to request this report.
The Statistical Profile Report allows you to compare your laboratory's statistics to the Peer, Method, and All Labs consensus group statistics for selected time periods. The Statistical Profile Report also provides two histograms summarizing how your laboratory's mean and CV compare to the range of mean and range of CVs calculated for each consensus group.
State of the Art
An analytical goal used to confine test imprecision within specified limits with the idea the imprecision for each test should be equal to or less than the best imprecision achievable by technology. State of the Art uses consensus group information from the Unity™ Interlaboratory Program.
The "best imprecision achievable" is defined as the imprecision calculated for a specific consensus group–Peer, Method, or All Labs. Peer is the ideal consensus group for comparison, but the Method and All Labs consensus groups provide alternatives when a representative Peer group is not available or the Peer group is unacceptably small.
summary data
The mean, SD, and number of points for a data set comprised of the control material results for testing an analyte over a specific time range (for example, October 2007).
suspect data
Data points violating any SPC rule or analytical goal set to reject or warn.
systematic error
A trend or shift away from the laboratory mean. Small amounts of systematic error are tolerable. Systematic error remains until corrective action is taken.
TE (total error)
Total error is the overall error that may occur in a test result due to the imprecision and bias present in the testing procedure. Use the following formula to calculate the TE:

TEa specifications are available from several sources as described in Determine Quality Requirements for the Test.
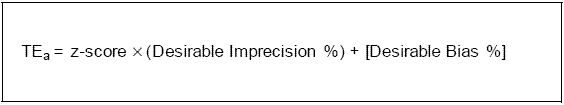
TEa (total allowable error)
Total allowable error is a quality requirement setting limits for the imprecision and bias allowable in a test result. After choosing a TEa, the TE budget can be calculated. Use the following formula to calculate the TEa:
Total Error-BV
An analytical goal used as a quality appraisal tool. Total Error-BV sets upper and lower limits of performance for each test based on the TEa using biological variation data and laboratory-selected performance goals. Total Error-BV provides feedback on laboratory bias, imprecision, and TE.
trend
A type of systematic error causing a gradual, often subtle increase or decrease in control values and possibly patient results.
Urinalysis Report
Note: The Urinalysis Report is optional. Contact your Bio‑Rad QC Program Representative to request this report.
Customers submitting data for a Bio-Rad urinalysis product to the Unity™ Interlaboratory Program receive a qualitative report consisting of the following:
The Urinalysis Report displays only one set of results per day. If submitting multiple sets, this report includes the one with the most recent date-time stamp.
warn rule
A SPC rule with a status of warn. When a data point violates a SPC rule with a warn status, the data point is accepted and is included in monthly and cumulative statistics and is reported to the Unity™ Interlaboratory Program for consensus group comparison.
Westgard rules
A laboratory QC system based on a set of six core statistical rules, each having statistical power to detect random and systematic deviations from the norm.
Worldwide Report
The Worldwide Report is provided through the Unity™ Interlaboratory Program. The Worldwide Report contains all Peer group and Method group statistics and is a good reference to use when evaluating a new instrument or kit. The Worldwide Report includes:
z-score
The z-score is the number of standard deviations a control result is from the expected mean. Use the following formula to calculate the z-score:

A z-score of ±2.3 indicates the observed value is ±2.3SD away from the expected mean. A data point with this z-score would violate the 1-2s rule, but not the 1-3s rule. The z-score appears on the Single Test Point Data Entry dialog box.